OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH
(OCCUPATIONAL FIRST AID)
(OCCUPATIONAL FIRST AID)
Assalamualaikum , we have given the new task for chapter 6. There are three members of this group discussion , which is me, MUHAMMAD AIZUDDIN AKMAL BIN ZALKAHA,MUHAMMAD HASIF AIMAN BIN IBRAHIM AND NUR AZAMULLAH BIN MOHAMED.
We are from group 'L.E.D.'
POISONING
Poisoning is injury or death due to swallowing, inhaling, touching or injecting various drugs, chemicals, venoms or gases. Many substances — such as drugs and carbon monoxide — are poisonous only in higher concentrations or dosages. And others — such as cleaners — are dangerous only if ingested. Children are particularly sensitive to even small amounts of certain drugs and chemicals.
TYPES OF POISONING
- If it is safe to do so, rescue the person from the danger of the gas, fumes, or smoke. Open windows and doors to remove the fumes.
- Take several deep breaths of fresh air, and then hold your breath as you go in. Hold a wet cloth over your nose and mouth.
- DO NOT light a match or use a lighter because some gases can catch fire.
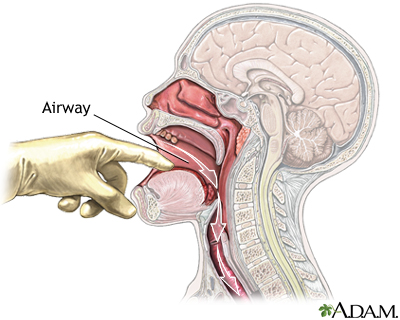
- After rescuing the person from danger, check and monitor the person's airway, breathing, and pulse. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
- If necessary, perform first aid for eye injuries or convulsion first aid.
- If the person vomits, clear the person's airway. Wrap a cloth around your fingers before cleaning out the mouth and throat.
- Even if the person seems perfectly fine, get medical help.
- DO NOT:
- Give an unconscious person anything by mouth.
- Induce vomiting unless you are told to do so by the Poison Control Center or a doctor. A strong poison that burns on the way down the throat will also do damage on the way back up.
- Try to neutralize the poison with lemon juice or vinegar, or any other substance, unless you are told to do so by the Poison Control Center or a doctor.
- Use any "cure-all" type antidote.
- Wait for symptoms to develop if you suspect that someone has been poisoned.
No comments:
Post a Comment